Iso stock options and amt
Ordinary income from incentive stock options, unlike wage income or income from NSOs, is also not subject to payroll taxes such as FICA. Note further that an employer generally does not claim a corporate income tax deduction which would be in an amount equal to the amount of income recognized by the employee upon the exercise of its employee's ISO, unless the employee does not meet the holding-period requirements and sells early, making a disqualifying disposition.
How AMT is Calculated
ISOs must be exercised by an employee within 3 months of termination of employment or be forfeited. Since it may be difficult or impossible to sell shares on the secondary market , this would often either force employees to pay a substantial alternative minimum tax liability, or forfeit their earned shares. To solve this issue, some private companies allow the option to convert ISOs to NSOs, which allows the exercise period to be extended to up to 10 years.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of created the 83 i election for tax year , which allows an employee of a company satisfying certain requirements to defer taxation upon exercise for up to 5 years. Note that the strike price for an employee's ISO grant must be set to the current a fair market value of the common shares, which is generally lower than that of the preferred valuation of shares owned by venture capitalists that is quoted in news.
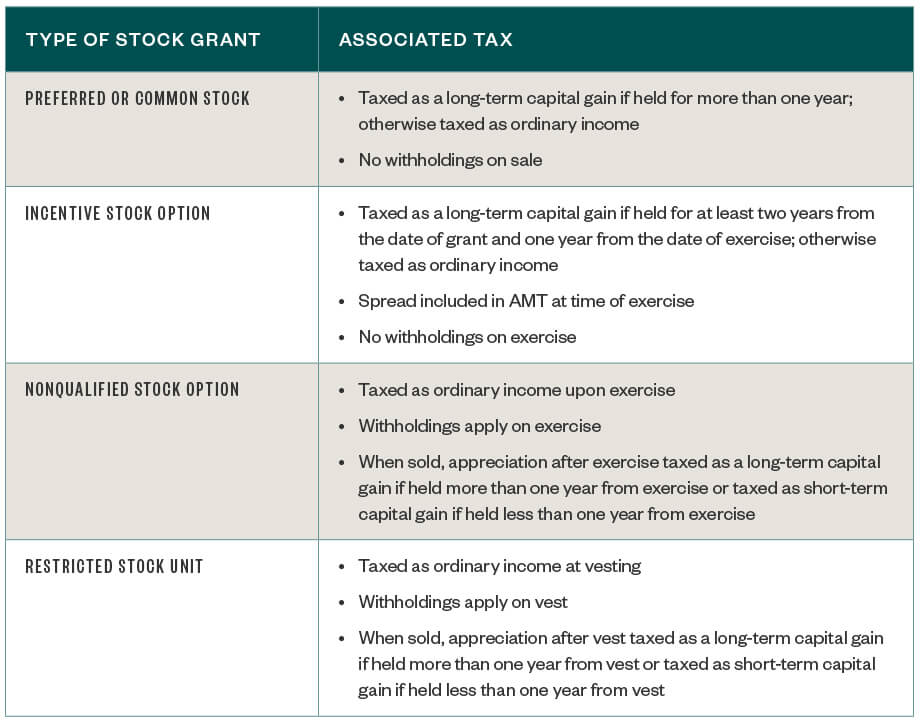
Equity 101 Part 3: How stock options are taxed
If the employee performs an early exercise and does not fully vest the shares, the exercise price for the unvested shares is returned. In this example, the employee does not early exercise. On February 1, , the employee elects to exercise, or purchase, these vested shares. These shares are now a disqualifying disposition because they were sold before a 1 year holding period. If the taxpayer paid AMT in , the taxpayer is may be entitled to recoup any AMT credit generated in tax year Additionally, there are several other restrictions which have to be met by the employer or employee in order to qualify the compensatory stock option as an ISO.
For a stock option to qualify as ISO and thus receive special tax treatment under Section a of the Internal Revenue Code the "Code" , it must meet the requirements of Section of the Code when granted and at all times beginning from the grant until its exercise.
The requirements include:. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Retrieved New York Times DealBook. The National Law Review. Archived from the original on Business Insider.
Stock Options and the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) | NCEO
Mark R. The New York Times. Report stock sale profits as a capital gain or report losses as a capital loss if both of these apply:.
The broker your employer uses to handle the stocks will send you a Form B. The form will include:. Read the B to see if the expenses related to the sale were excluded from the reported proceeds. You might receive a statement from your employer showing the amount included in your W-2 income if any. You might exercise the option and not sell the stock in the same year you exercised it.
Refundable AMT Credit for Employee Stock Option Taxes
For AMT purposes, your gain will be lower — or your loss will be greater — than for regular income tax purposes. Keep a record of the AMT basis in your files so that you can correctly figure the AMT gain or loss when you sell the stock.
Your employer must give you Form by Jan. Do you know how to report taxes on stock option sales? This link is to make the transition more convenient for you. You should know that we do not endorse or guarantee any products or services you may view on other sites. Tax information center : Income : Investments.